Matter consists of elements and compounds
1. def matter: mass and space.
2. def elements: the distinctive building blocks of matter
3. def compounds
4. four elements make up our body weight(oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen)
stuff材料,原料
distinctive有特色的,特殊的
compound混合物;化合物
phosphorus KK:[







 ]磷
]磷








 ]磷
]磷chlorine KK:[





 ]氯
]氯






 ]氯
]氯fluorine KK:[







 ]氟
]氟








 ]氟
]氟bromine KK:[



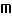

 ]溴
]溴






 ]溴
]溴sodium KK:[





 ]鈉
]鈉






 ]鈉
]鈉calcium KK:[






 ]鈣
]鈣







 ]鈣
]鈣arsenic KK:[





 ]砷
]砷






 ]砷
]砷uranium KK:[







 ]鈾
]鈾
Atoms, ions, and molecules are the building blocks of matter
5. def atom: smallest unit of matter, still retain its chemical properties. atomic theory
6. atom cotains a certain number of subatomic particles: proton質子, neutron, and electron
7. def nucleus原子核, atomic number原子序, mass number質量數,isotope同位素.
8. ion離子, pH(hydrogen ion and hydroxide ion), neutral solution溶液, acidic solution, basic solution
9. organic compounds: hydrocarbons碳氫化合物, chlorinated hydrocarbons含氯碳氫化合物, simple carbonhydrates 碳水化合物
molecule分子
superscript上標(寫在上方的符號或文字)
nitrate硝酸鹽
soared猛增;暴漲
compound化合物
sodium鈉
chloride氯化物
chemical formula化學式
octane辛烷
glucose葡萄糖
lipid脂質
Some forms of matters are more useful than orhters
10. matter quality base on its availability and concentration
2-3How can matter change?
Matter undergoes physical, chemical, and nuclear changes
1. def physical change, chemical change(chemical reaction)
2. three type of nuclear change: natural radioactive decay放射性自然衰變, nuclear fission核分裂, nuclear fusion核融合
foil箔,金屬薄片
spontaneously自然地;自發地
chunk相當大的部分(或數量)
核衰變
226/88Ra → 222/86Rn + 4/2He(alfa)
32/15P→32/16S+β (beta)
55/26Fe+e-→55/25Mn (beta)
60/27Co→60/28Ni+γ+γ (gamma)
核分裂 n + U235 -> Ba143 + Kr91 + 2n
核融合 H2 + H3 -> He4 + n
元素週期表 (wiki) s32(textbook)
We cannot create or destroy matter
3. law of conservation of matter物質守恆(不滅)定律








 ]鈾
]鈾Atoms, ions, and molecules are the building blocks of matter
5. def atom: smallest unit of matter, still retain its chemical properties. atomic theory
6. atom cotains a certain number of subatomic particles: proton質子, neutron, and electron
7. def nucleus原子核, atomic number原子序, mass number質量數,isotope同位素.
8. ion離子, pH(hydrogen ion and hydroxide ion), neutral solution溶液, acidic solution, basic solution
9. organic compounds: hydrocarbons碳氫化合物, chlorinated hydrocarbons含氯碳氫化合物, simple carbonhydrates 碳水化合物
molecule分子
superscript上標(寫在上方的符號或文字)
nitrate硝酸鹽
soared猛增;暴漲
compound化合物
sodium鈉
chloride氯化物
chemical formula化學式
octane辛烷
glucose葡萄糖
lipid脂質
Some forms of matters are more useful than orhters
10. matter quality base on its availability and concentration
2-3How can matter change?
Matter undergoes physical, chemical, and nuclear changes
1. def physical change, chemical change(chemical reaction)
2. three type of nuclear change: natural radioactive decay放射性自然衰變, nuclear fission核分裂, nuclear fusion核融合
foil箔,金屬薄片
spontaneously自然地;自發地
chunk相當大的部分(或數量)
核衰變
226/88Ra → 222/86Rn + 4/2He(alfa)
32/15P→32/16S+β (beta)
55/26Fe+e-→55/25Mn (beta)
60/27Co→60/28Ni+γ+γ (gamma)
核分裂 n + U235 -> Ba143 + Kr91 + 2n
核融合 H2 + H3 -> He4 + n
元素週期表 (wiki) s32(textbook)
We cannot create or destroy matter
3. law of conservation of matter物質守恆(不滅)定律

